Nipah Virus Claims Life of Young Boy in Kerala
In a disturbing chain of events, a 14-year-old boy from southern India's Kerala state has succumbed to the lethal Nipah virus, sparking a surge in preventive measures from state authorities. The boy tragically lost his life following a cardiac arrest, marking the beginning of an intense response to this potentially epidemic-triggering virus.
Kerala, a state previously affected by the Nipah virus, is no stranger to the challenges posed by this deadly pathogen. The state's health minister, Veena George, reported that 60 individuals have been categorized as high-risk contacts. These people are being closely monitored to prevent the virus from spreading further. The state has swung into action with the establishment of 25 specialized committees aimed at identifying and isolating those who may have been exposed to the virus.
Preventive Measures and Healthcare Initiatives
Dr. Anoop Kumar, who heads critical care medicine at Aster MIMS Hospital in Calicut, highlighted that the positive diagnosis in the school-going boy has put authorities on high alert. The government is intensely tracking the 214 primary contacts identified, with the priority being the 60 high-risk cases.
Isolation wards have been set up across health institutions in Kerala to treat any potential patients, reflecting the state's proactive approach to containing the outbreak. Family members of the affected boy have also been under observation at a local hospital, and those who had potential exposure have been instructed to home quarantine.
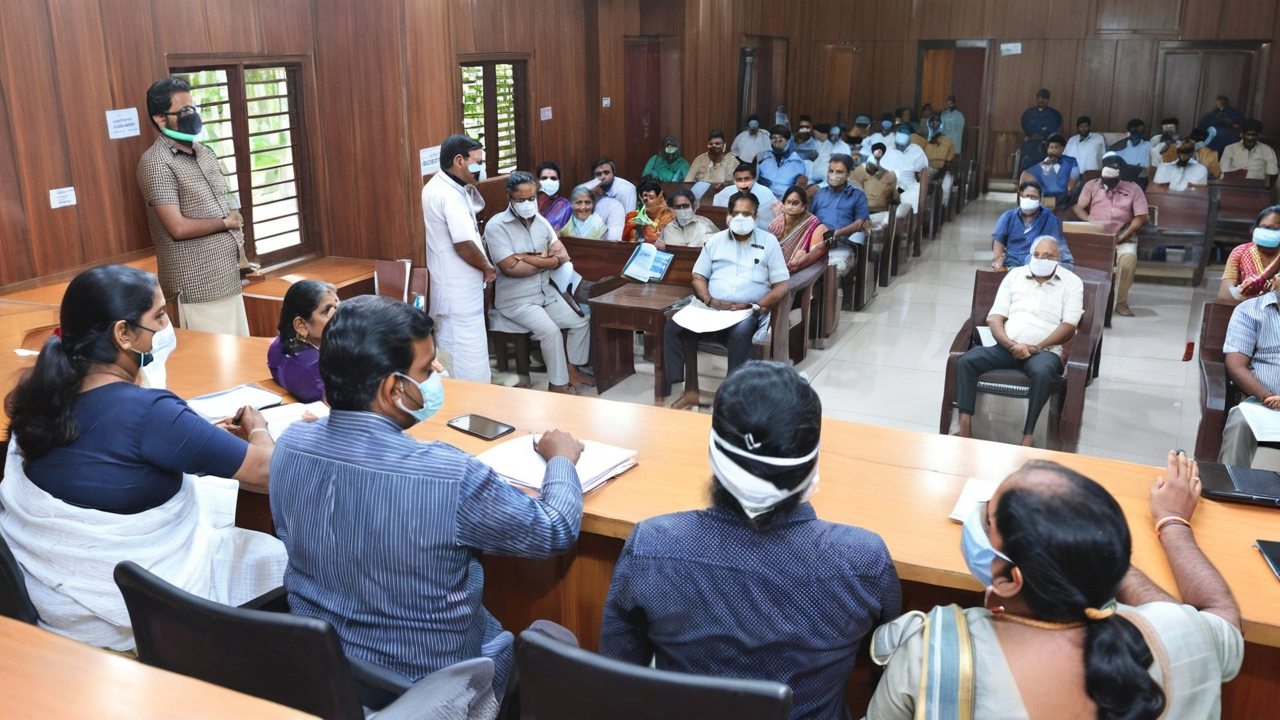

A Coordinated Response to a Priority Pathogen
The lethality of the Nipah virus cannot be understated. Classified as a priority pathogen by the World Health Organisation (WHO), the virus is notorious for its lack of vaccines or cures. This severe pathogen can lead to encephalitis, or brain-swelling fever, which is often fatal. The seriousness of the outbreak has compelled Kerala’s health system to act decisively.
Health authorities are working meticulously to trace and isolate any individuals who may have contracted the virus. The goal is to contain this outbreak swiftly to prevent a widespread health crisis. This incident underscores the broader challenges posed by zoonotic diseases - pathogens that jump from animals to humans and can lead to devastating outbreaks.
Continuing Vigilance and Public Health
Since its first appearance in Kerala in 2018, the Nipah virus has been linked to numerous deaths, highlighting the persistent threat it poses. Past outbreaks have taught crucial lessons on the importance of quick response, rigorous contact tracing, and widespread awareness campaigns aimed at educating the public on necessary preventive measures.
While the health minister’s announcement has set off alarms, it has also galvanized the health department, local hospitals, and the community at large. The state's history with the virus has fostered a readiness and an urgency that can be seen in the prompt establishment of isolation wards and the coordinated effort to monitor all potential contacts.
The challenge, however, remains immense. Efforts to monitor and contain the virus are ongoing, with top health officials in continuous meetings to refine their strategies. Their proactive stance involves not just treating the infected but also employing preventive measures to stop further transmission.
Lessons from Past Outbreaks
The recurrent nature of Nipah virus outbreaks in Kerala serves as a sobering reminder of the importance of vigilance in public health. Previous experiences have reinforced the necessity for rapid response, detailed contact tracing, and public education on hygiene and preventive practices.
The lack of vaccines and treatment options puts a premium on preventive measures and timely intervention. This is where the establishment of dedicated committees and isolation wards becomes crucial. Authorities are also leveraging community healthcare workers to educate the public, distribute protective equipment, and enforce quarantine measures where necessary.
These preventive steps, however, require more than just logistical arrangements; they demand public cooperation and adherence to health advisories. The community’s role in adhering to guidelines, reporting symptoms promptly, and cooperating with health monitoring can significantly influence the outbreak's trajectory.
A Coordinated Public Health Effort
The Kerala government’s multi-faceted strategy involves not just medical interventions but also social strategies aimed at minimizing panic and misinformation. This includes regular updates from health officials, transparent communication channels, and support systems for affected families.
As the state navigates this outbreak, the collective effort of healthcare workers, government officials, and the community will be instrumental in curbing the virus's spread. The incident underscores the need for ongoing public health readiness, especially as new infectious diseases continue to emerge globally.
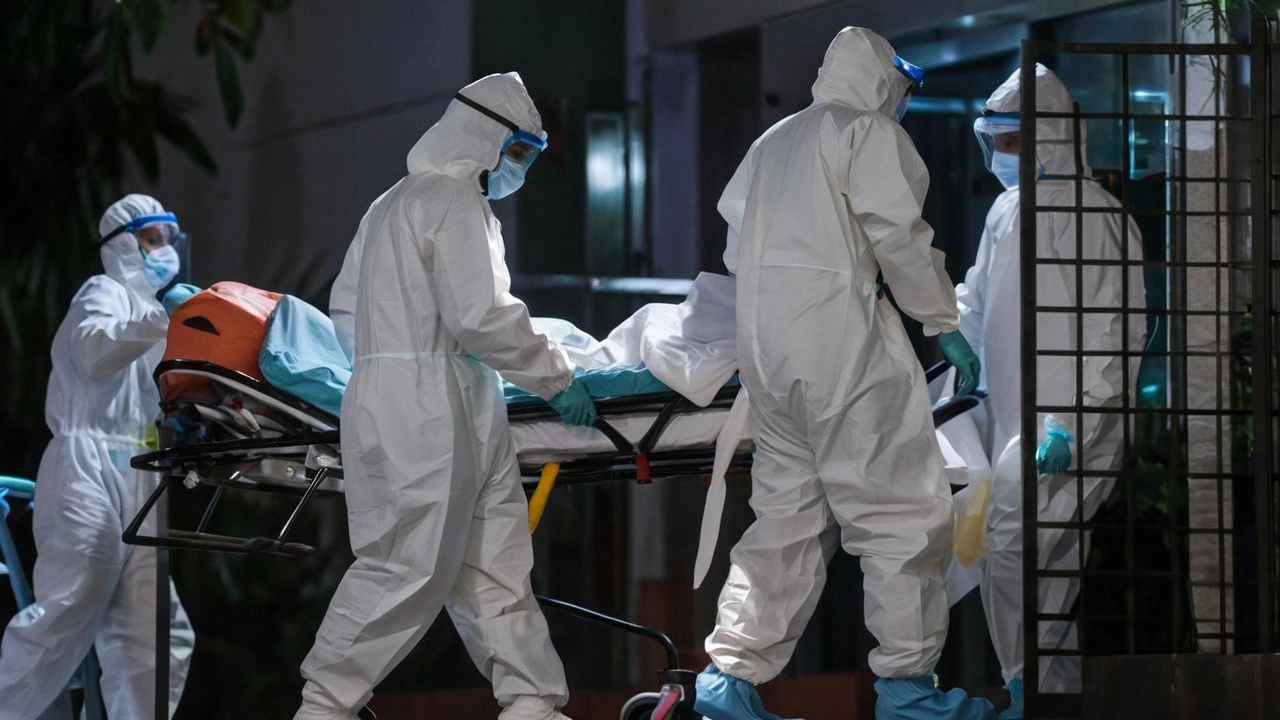

Future Preparedness and Public Awareness
Looking ahead, Kerala’s response to the Nipah virus highlights the critical elements of outbreak management: rapid identification, effective isolation, public education, and continuous monitoring. The state’s proactive measures, while stringent, are aimed at safeguarding public health and preventing further tragedies.
Ongoing research into the Nipah virus also continues to be a priority. Scientists and healthcare researchers are working tirelessly to understand the virus better and develop potential cures or vaccines. Until then, vigilance and public cooperation remain the cornerstone of efforts to prevent and contain future outbreaks.







Posts Comments
Aaron Leclaire July 24, 2024 AT 12:30
This is just another case of overblown media panic. One dead kid and they're acting like the apocalypse is coming.
Mitch Roberts July 25, 2024 AT 07:11
bro the way kerala handles this is insane 🤯 like they literally have teams on standby, isolation wards prepped, and people checking in on contacts like it's a daily checkup. we need this energy in the us. stop waiting for the next pandemic to hit before you do something. 🙏
Mark Venema July 26, 2024 AT 01:05
The systematic response by Kerala's public health infrastructure is a textbook example of effective outbreak containment. The establishment of specialized committees, rigorous contact tracing, and proactive isolation protocols demonstrate a high level of preparedness. This model should be studied and replicated globally, particularly in regions with limited healthcare resources.
Brian Walko July 27, 2024 AT 19:35
Kerala's approach is exactly what we need more of - calm, coordinated, and community-centered. The fact that they're using local healthcare workers to educate and enforce safety measures shows deep trust between the system and the people. That’s not just policy, that’s public health wisdom.
Derrek Wortham July 29, 2024 AT 16:20
You know what’s really scary? That this virus came from bats again. And no one talks about how the real problem is deforestation pushing wildlife into human spaces. They’re monitoring 60 people? What about the 60,000 people living near forests who don’t even know what a Nipah virus is? This isn’t a health crisis - it’s a crime against ecology.
Deepti Chadda July 29, 2024 AT 23:49
India still the best in the world at handling outbreaks 🇮🇳 no other country moves this fast. kerala team deserves a national award. no panic just action. #ProudIndian
Anjali Sati July 30, 2024 AT 02:43
They say '60 high-risk contacts' but how many of those are actually being tested? And who's paying for the isolation? Hospitals are already broke. This looks good on paper but in practice? Half the people probably ignore quarantine. We've seen this movie before.
Write a comment